정밀 육각 스탠드오프 부품의 복합 절삭 가공 공정

CNC 가공에서의 엔드밀 적용
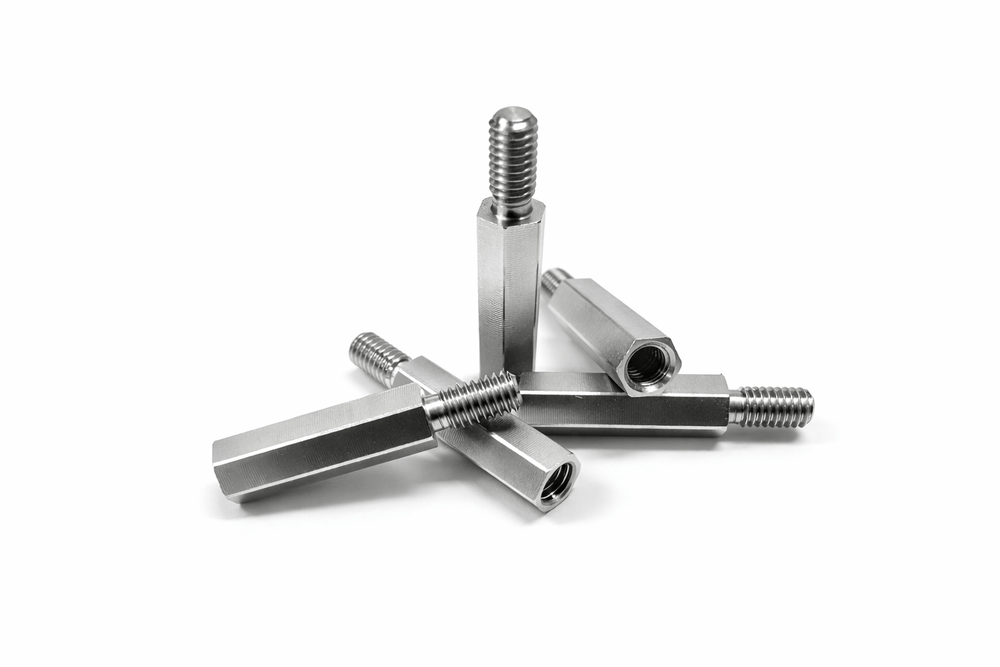
현대 정밀 제조 산업에서 육각 형태를 포함한 복합 형상의 부품은 항공우주, 반도체 장비, 정밀 의료기기 등 다양한 분야에서 핵심적인 역할을 수행하고 있습니다. 특히 육각 스탠드오프(Hexagonal Standoff) 부품은 단순한 체결 부품을 넘어, 부품 간의 간격을 정밀하게 유지하고 구조적 안정성을 확보하는 데 필수적인 요소입니다. 이러한 부품을 제작하기 위해서는 CNC(Computer Numerical Control) 선반 공정과 엔드밀(End-mill)을 이용한 밀링 공정이 고도로 결합된 복합 가공 기술이 요구됩니다.
고정밀 부품 제조를 위한 CNC 선삭 및 밀링 복합 가공
정밀 가공 부품의 제작은 기본적으로 원통형 소재를 회전시켜 외경을 가공하는 CNC 선삭(Turning) 공정에서 시작됩니다. 본 부품의 나사부(Threaded Part)와 단차 영역은 CNC 선반의 고속 회전과 정밀 이송 제어를 통해 수 마이크로미터(μm) 단위의 오차 범위 내에서 성형됩니다. 특히 나사산의 피치(Pitch)와 유효 지름은 체결 강도와 직결되므로, 절삭 속도와 공구 진입각에 대한 정밀 계산이 필수적입니다.
육각 형상을 갖는 몸체 부분은 엔드밀을 이용한 측면 절삭을 통해 완성됩니다. 이 공정은 흔히 ‘육각 치기’ 또는 ‘폴리곤 가공(Polygon Turning)’으로 불리며, 다축 제어가 가능한 CNC 복합 가공기에서 주축과 공구 주축의 회전을 정밀하게 동기화하여 평면을 생성합니다. 엔드밀의 날수가 증가할수록 절삭 시 발생하는 진동(Chatter)을 억제할 수 있으며, 이를 통해 표면 거칠기(Surface Roughness)를 향상시켜 거울과 같은 금속 광택을 구현할 수 있습니다.
육각 형상 가공에서의 엔드밀 절삭 메커니즘
엔드밀을 이용한 측면 절삭 공정은 고속 회전하는 절삭날이 소재의 측면을 순차적으로 제거하는 방식으로 이루어집니다. 육각 각면이 정확히 120° 기하 정밀도를 유지하기 위해서는 CNC 컨트롤러의 분할대(Indexing) 기능이 매우 정밀하게 작동해야 합니다. 이 과정에서 발생하는 절삭열은 공구 수명과 부품의 열변형에 영향을 미치므로, 고성능 절삭유(Coolant)를 사용한 냉각과 칩(Chip)의 효과적인 배출 관리가 필수적입니다.
특히 모서리부에서 발생하는 버(Burr)를 최소화하기 위해 상향 절삭(Up-cut)과 하향 절삭(Down-cut)을 경로 최적화 방식으로 조합 적용하며, 고경도 스테인리스강이나 티타늄 합금을 가공할 경우에는 코팅된 초경 엔드밀(Coated Carbide End-mill)을 사용하여 공구 마모를 최소화하고 장시간 안정적인 가공 품질을 유지합니다.
재료 선택과 가공 특성
육각 스탠드오프 가공에는 주로 스테인리스 스틸, 티타늄, 알루미늄이 사용됩니다.
스테인리스 스틸은 내식성이 뛰어나지만 가공성이 낮기 때문에 적절한 절삭 속도와 피드율 설정이 중요합니다. 예를 들어, 절삭 속도(Vc)는 140~160 SFM 범위가 일반적이며, 티타늄 합금의 경우 헬릭스 각도 45° 엔드밀을 사용하여 열 저항성과 칩 배출성을 향상시킵니다. 최근에는 태그치(Taguchi) 기법, TOPSIS 분석, 개미사자 최적화(ALO) 등과 같은 통계적·알고리즘 기반의 최적화 기법을 적용하여 표면 조도와 공구 마모를 동시에 개선하는 연구와 적용 사례가 확대되고 있습니다.
CNC 가공에서의 엔드밀 적용
현대 정밀 제조 산업에서 육각 형태를 포함한 복합 형상의 부품은 항공우주, 반도체 장비, 정밀 의료기기 등 다양한 분야에서 핵심적인 역할을 수행하고 있습니다. 특히 육각 스탠드오프(Hexagonal Standoff) 부품은 단순한 체결 부품을 넘어, 부품 간의 간격을 정밀하게 유지하고 구조적 안정성을 확보하는 데 필수적인 요소입니다. 이러한 부품을 제작하기 위해서는 CNC(Computer Numerical Control) 선반 공정과 엔드밀(End-mill)을 이용한 밀링 공정이 고도로 결합된 복합 가공 기술이 요구됩니다.
고정밀 부품 제조를 위한 CNC 선삭 및 밀링 복합 가공
정밀 가공 부품의 제작은 기본적으로 원통형 소재를 회전시켜 외경을 가공하는 CNC 선삭(Turning) 공정에서 시작됩니다. 본 부품의 나사부(Threaded Part)와 단차 영역은 CNC 선반의 고속 회전과 정밀 이송 제어를 통해 수 마이크로미터(μm) 단위의 오차 범위 내에서 성형됩니다. 특히 나사산의 피치(Pitch)와 유효 지름은 체결 강도와 직결되므로, 절삭 속도와 공구 진입각에 대한 정밀 계산이 필수적입니다.
육각 형상을 갖는 몸체 부분은 엔드밀을 이용한 측면 절삭을 통해 완성됩니다. 이 공정은 흔히 ‘육각 치기’ 또는 ‘폴리곤 가공(Polygon Turning)’으로 불리며, 다축 제어가 가능한 CNC 복합 가공기에서 주축과 공구 주축의 회전을 정밀하게 동기화하여 평면을 생성합니다. 엔드밀의 날수가 증가할수록 절삭 시 발생하는 진동(Chatter)을 억제할 수 있으며, 이를 통해 표면 거칠기(Surface Roughness)를 향상시켜 거울과 같은 금속 광택을 구현할 수 있습니다.
육각 형상 가공에서의 엔드밀 절삭 메커니즘
엔드밀을 이용한 측면 절삭 공정은 고속 회전하는 절삭날이 소재의 측면을 순차적으로 제거하는 방식으로 이루어집니다. 육각 각면이 정확히 120° 기하 정밀도를 유지하기 위해서는 CNC 컨트롤러의 분할대(Indexing) 기능이 매우 정밀하게 작동해야 합니다. 이 과정에서 발생하는 절삭열은 공구 수명과 부품의 열변형에 영향을 미치므로, 고성능 절삭유(Coolant)를 사용한 냉각과 칩(Chip)의 효과적인 배출 관리가 필수적입니다.
특히 모서리부에서 발생하는 버(Burr)를 최소화하기 위해 상향 절삭(Up-cut)과 하향 절삭(Down-cut)을 경로 최적화 방식으로 조합 적용하며, 고경도 스테인리스강이나 티타늄 합금을 가공할 경우에는 코팅된 초경 엔드밀(Coated Carbide End-mill)을 사용하여 공구 마모를 최소화하고 장시간 안정적인 가공 품질을 유지합니다.
재료 선택과 가공 특성
육각 스탠드오프 가공에는 주로 스테인리스 스틸, 티타늄, 알루미늄이 사용됩니다.
스테인리스 스틸은 내식성이 뛰어나지만 가공성이 낮기 때문에 적절한 절삭 속도와 피드율 설정이 중요합니다. 예를 들어, 절삭 속도(Vc)는 140~160 SFM 범위가 일반적이며, 티타늄 합금의 경우 헬릭스 각도 45° 엔드밀을 사용하여 열 저항성과 칩 배출성을 향상시킵니다. 최근에는 태그치(Taguchi) 기법, TOPSIS 분석, 개미사자 최적화(ALO) 등과 같은 통계적·알고리즘 기반의 최적화 기법을 적용하여 표면 조도와 공구 마모를 동시에 개선하는 연구와 적용 사례가 확대되고 있습니다.
엔드밀 유형 비교
| 엔드밀 유형 | 주요 특징 | 적용 분야 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 스퀘어 엔드밀 | 평평한 끝단, 2~4 플루트 | 슬롯팅, 프로파일링 | 범용성 높음, 평면 정밀 | 곡면 가공 제한 |
| 볼 노즈 엔드밀 | 둥근 끝단 | 3D 윤곽, 복잡형상 | 매끄러운 곡면 구현 | 칩 배출 어려움 |
| 슬롯 드릴 | 오프셋 끝단 | 키웨이, 슬롯 가공 | 플런지 컷팅 유리 | 깊은 가공 제한 |
| 마이크로 엔드밀 | 초소형 직경 | 미세 구조 | 고정밀 | 플로잉 현상 가능 |
| 헬리컬 커터 | 다중 인서트 | 고속 러핑 | MRR 향상 | 고강성 설비 필요 |
표면 마감과 공차 관리
CNC 엔드밀 가공에서 표면 거칠기 기준은 일반적으로 Ra 3.2μm(125μin) 수준이며, 고정밀 가공 시 ±0.002mm 공차까지 달성 가능합니다. 업밀링과 클라임 밀링을 적절히 조합하면 칩 두께 및 열 전달을 효과적으로 제어할 수 있으며, 공구 코팅은 마모 감소 및 표면 품질 유지에 큰 역할을 합니다. 5축 CNC 장비를 사용하면 복잡 형상에서도 공차 안정성을 강화할 수 있으며, 열 변형 보정 기능을 통해 반복 정밀도를 향상시킵니다.
| 가공 매개변수 | 스테인리스 스틸 (예: 316) | 티타늄 합금 (예: Ti-6Al-4V) | 알루미늄 | 최적화 팁 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 절삭 속도 (SFM) | 140~160 | 160 | 500 | 열 저항 고려, 코팅 사용 |
| 피드율 (IPT) | 0.002~0.004 | 0.001~0.003 | 0.005~0.010 | 칩 로드 최적화 |
| 축방향 깊이 (ADOC) | 0.5~1.0D (D: 직경) | 0.3~0.6D | 1.0~1.5D | HEM 기법 적용 |
| 방사형 깊이 (RDOC) | 0.1~0.2D | 0.05~0.1D | 0.2~0.3D | 채터 방지 |
| MRR (in³/min) | 63.6 (예: 1/2인치 공구) | 45.2 | 80.5 | 피드 증가로 27% 향상 |
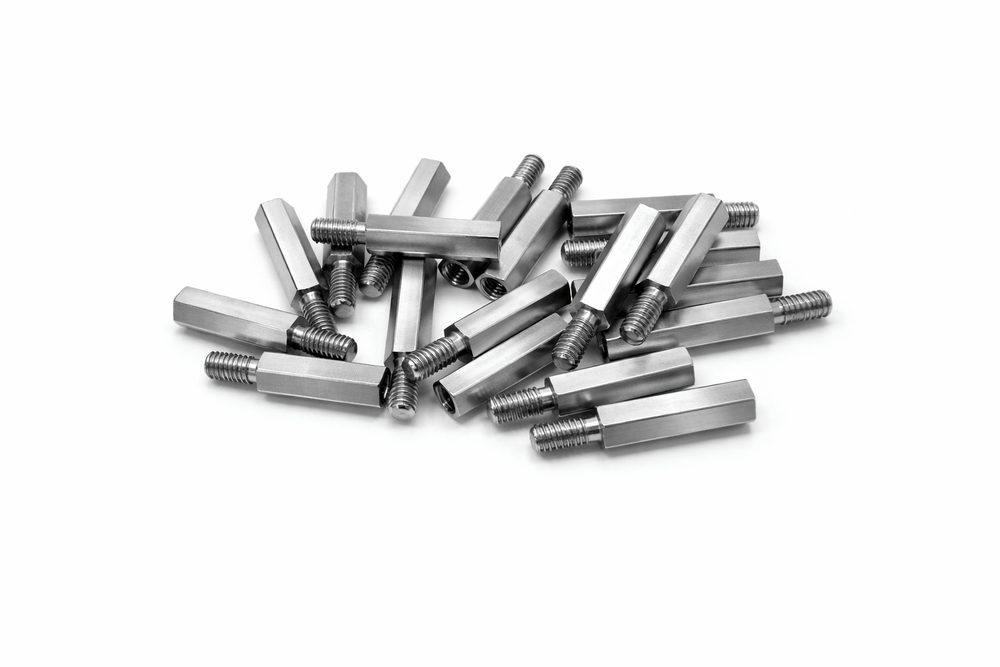
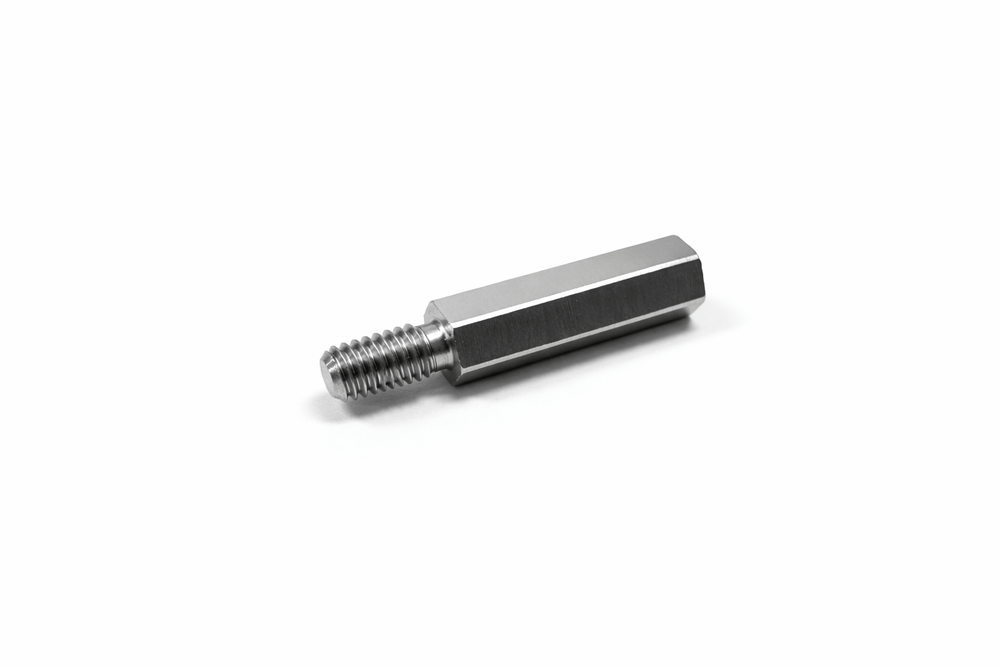


적용 분야
전자 산업에서 육각 스탠드오프는 PCB 고정 및 절연 간격 유지 부품으로 널리 사용되며, 대량 생산 환경에서도 CNC 복합 가공 기술을 통해 높은 정밀도와 생산성을 동시에 충족합니다. 육각부의 날카로운 모서리와 매끄러운 평면은 엔드밀의 고속 회전과 정밀 이송 제어가 완벽하게 동기화된 결과물이며, 이는 반복적인 체결 및 분해 조건에서도 마모가 최소화되는 장점을 제공합니다. 육각 스탠드오프와 같은 정밀 체결 부품은 단순한 기계 요소가 아니라, CNC 선삭과 엔드밀 밀링 기술이 융합된 고난이도 CNC 정밀가공의 결과물입니다. 공정 조건, 재료 특성, 절삭 공구, 공차 관리가 유기적으로 결합될 때 비로소 안정적이고 신뢰성 높은 품질을 확보할 수 있습니다.

Precision Hexagonal Standoff Component — Hybrid Machining Process
Application of End-Mill Cutting in CNC Machining
In modern precision manufacturing industries, components with complex geometries—including hexagonal profiles—play a critical role across sectors such as aerospace, semiconductor equipment, and advanced medical devices. Among them, hexagonal standoff components are essential not only for mechanical fastening but also for precisely maintaining spacing between parts and ensuring structural stability.
To manufacture these components, a hybrid machining approach combining CNC turning and end-mill-based milling operations is required, enabling highly accurate and repeatable geometric precision.
CNC Turning and Milling Hybrid Machining for High-Precision Parts
Production of precision components typically begins with CNC turning, where a cylindrical raw material rotates while its outer diameter is machined. The threaded section and stepped geometry of the part are formed using high-speed spindle rotation and precise feed-rate control, achieving tolerances within micron-level accuracy. Thread pitch and effective diameter directly influence fastening strength, making accurate calculation of cutting speed and tool entry angle critical.
The hexagonal body portion is then machined using side-cut end-milling. This process—often referred to as hex-cutting or polygon machining—is performed on multi-axis CNC hybrid machines where both the work spindle and tool spindle rotations are synchronized. Increasing the number of cutting flutes helps suppress chatter vibration, improving surface roughness and achieving a mirror-like metallic finish.
End-Mill Cutting Mechanism in Hexagonal Geometry Machining
During side-cut milling, the rotating cutting edges remove material sequentially along the hexagonal surfaces. To maintain the exact 120-degree geometry between each face, the CNC controller’s indexing accuracy is crucial. Cutting heat must be controlled to prevent thermal deformation and tool wear, making the application of high-performance coolant and effective chip evacuation essential.
To minimize burr formation along edges, optimized tool paths combining both up-cut and down-cut strategies are applied. For high-hardness stainless steels and titanium alloys, coated carbide end mills are used to extend tool life and maintain dimensional accuracy over prolonged machining cycles.
Material Selection and Machinability Considerations
Hexagonal standoffs are commonly produced using stainless steel, titanium, or aluminum.
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance but relatively poor machinability, requiring careful optimization of cutting parameters such as cutting speed and feed rate. For example, cutting speeds of 140–160 SFM are typical for stainless steels, while titanium machining benefits from the use of 45-degree helix end mills to improve heat resistance and chip evacuation.
In recent years, Taguchi methods, TOPSIS analysis, and Ant Lion Optimization (ALO) have been widely applied to simultaneously improve surface finish and tool-wear performance, strengthening parameter optimization in industrial applications.
Comparison of End-Mill Types
| End-Mill Type | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Square End Mill | Flat end tip, 2–4 flutes | Slotting, profiling | Highly versatile, excellent flat-surface finish | Limited curved-surface capability |
| Ball Nose End Mill | Rounded tip | 3D contour & complex shapes | Smooth surface finishing on curves | Difficult chip evacuation |
| Slot Drill | Offset flat end | Keyway & slot machining | Suitable for plunge cutting, minimal deflection | Not ideal for deep cutting |
| Micro End Mill | Ultra-small diameter tools | Micro-structures, miniature parts | Extreme precision & nano-scale finishing | Possible ploughing effect |
| Helical Cutter | Multi-insert design | High-speed roughing | Increased MRR & extended tool life | Requires high-rigidity equipment |
Surface Finish and Tolerance Control
In CNC end-milling, surface roughness standards commonly target Ra 3.2 μm (125 μin), while ultra-precision machining may achieve tolerances of ±0.002 mm. Combining up-milling and climb milling allows better thermal and chip-thickness control. Tool coatings also help minimize wear and maintain consistent surface finish quality.
In complex geometries, 5-axis CNC machining enhances tolerance stability, while thermal-compensation systems improve repeatability under varying machining conditions.
Recommended Machining Parameters
| Machining Parameter | Stainless Steel (e.g., 316) | Titanium Alloy (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V) | Aluminum | Optimization Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed (SFM) | 140–160 | 160 | 500 | Consider heat resistance & coating selection |
| Feed Rate (IPT) | 0.002–0.004 | 0.001–0.003 | 0.005–0.010 | Optimize chip load |
| Axial Depth of Cut (ADOC) | 0.5–1.0D | 0.3–0.6D | 1.0–1.5D | Apply HEM strategy |
| Radial Depth of Cut (RDOC) | 0.1–0.2D | 0.05–0.1D | 0.2–0.3D | Prevent chatter |
| MRR (in³/min) | 63.6 (1/2″ tool example) | 45.2 | 80.5 | Feed increase may enhance MRR by 27% |
Industrial Applications
In the electronics sector, hexagonal standoffs are widely used for PCB mounting and insulation spacing. Even in mass-production environments, CNC hybrid machining technologies enable both high productivity and precision stability. The sharply defined hexagonal edges and smooth flat surfaces are proof of synchronized high-speed cutting and precision feed-rate control.
These components are not simply hardware elements; they represent the integration of CNC turning and precision end-milling technology. When machining parameters, material properties, tooling, and tolerance management are harmonized, stable and highly reliable product quality can be consistently achieved.
추가 정보
정밀 육각 스탠드오프는 조립 기준면을 확보하면서 PCB/하우징 간 간격을 일정하게 유지하는 구조·연결 부품입니다. precision hexagonal standoff CNC endmill machining에서는 육각 외형의 대면폭(AF), 양단 기준면 평행도, 탭/내경 동심도, 모서리 디버링이 조립 품질과 반복 체결 안정성에 직접 영향을 줍니다.
핵심 포인트
- 육각 대면폭(AF) 공차는 렌치 체결성, 회전 미끄럼, 조립 토크 분산에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
- 양단 기준면 평행도/직각도는 스탠드오프가 “기준 높이” 역할을 할 때 평탄도와 조립 뒤틀림을 좌우합니다.
- 내경/탭 동심도 불량은 볼트 체결 시 편심 하중을 만들어 장기 풀림과 나사 마모 리스크를 키울 수 있습니다.
- 엔드밀 가공의 공구 마모는 육각 코너 라운딩과 치수 편차로 나타나므로 공구 교체 기준이 중요합니다.
- 버(burr)와 모서리 샤프는 손상 및 간섭 원인이 될 수 있어 디버링/미세 R 기준을 도면에서 명확히 두는 편이 좋습니다.
- 표면 거칠기와 가공결 방향은 외관뿐 아니라 체결 마찰 계수와 전도 경로 접촉면에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
- 소재(황동/알루미늄/스테인리스)별 열팽창과 강성 차이는 토크-클램핑력 관계를 바꿀 수 있습니다.
FAQ
육각 스탠드오프에서 가장 민감한 치수는 무엇인가요?
대면폭(AF)과 전체 길이(스페이서 높이), 양단 기준면의 평행도가 조립 품질에 가장 자주 영향을 줍니다. 특히 다수 체결 포인트를 가진 PCB 조립에서는 미세 편차가 누적되어 기판 뒤틀림으로 나타날 수 있습니다.
엔드밀로 육각 외형을 가공할 때 흔한 불량은 무엇인가요?
공구 마모로 인한 코너 라운딩, AF 편차 확대, 면 직진도(평탄) 저하가 대표적입니다. 가공 중 흔들림이 있으면 면마다 치수가 달라져 렌치 체결감이 불균일해질 수 있습니다.
육각 코너를 날카롭게 유지하는 것이 항상 좋은가요?
코너가 지나치게 날카로우면 버 잔류와 손상 위험이 커질 수 있습니다. 체결성과 안전성을 함께 보려면 미세 R 또는 디버링 기준을 기능 요구에 맞춰 설정하는 편이 안정적입니다.
탭(내나사) 정밀도는 어떤 항목이 중요하나요?
유효 나사 깊이, 탭 구멍의 가공 편심, 시작부 리드(lead) 상태가 체결 안정성과 반복 체결 내구성에 영향을 줍니다. 나사 체결부는 공차 누적의 영향을 크게 받으므로 기준면과 동심도 관리가 함께 필요합니다.
양단 평행도가 나쁘면 어떤 문제가 생기나요?
스탠드오프가 기판/하우징 기준을 동시에 잡는 구조에서 뒤틀림과 국부 응력 집중이 발생할 수 있습니다. 체결 토크를 올려도 하중이 고르게 분산되지 않아 풀림이나 파손 리스크가 커질 수 있습니다.
소재별로 공정이나 품질 기준이 달라지나요?
황동은 절삭성이 좋지만 표면 관리와 버 억제 기준이 중요해질 수 있고, 알루미늄은 흠집과 변형에 민감할 수 있습니다. 스테인리스는 공구 마모가 빨라 치수 편차가 커질 수 있어 공정 창과 검사 빈도 설정이 실무적으로 중요해집니다.
스탠드오프의 표면 거칠기는 조립에 영향을 주나요?
거칠기는 체결 마찰과 렌치 접촉면의 미끄럼, 외관 품질에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다. 전도 경로 역할을 겸하는 경우에는 접촉면 산화·오염과 결합되어 전기적 안정성에도 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
검사에서는 무엇을 우선 확인하는 편이 좋나요?
AF, 전체 길이, 양단 평행도, 나사 게이지(Go/No-Go), 버/모서리 상태를 우선 확인하는 흐름이 일반적입니다. 조립 불량이 반복된다면 동심도와 기준면 설정(측정 기준)을 함께 재검토하는 편이 효율적입니다.
관련 주제 확장
1) AF 공차와 체결 토크: 렌치 체결성의 기본
육각 대면폭(AF)이 좁아지면 렌치가 헛도는 현상이 증가할 수 있고, 넓어지면 조립 공구 호환성이 떨어질 수 있습니다. AF 편차는 면마다 다르게 나타날 수 있어, 측정 위치와 기준을 일관되게 두는 편이 중요합니다. 공구 마모와 소재 경도는 AF 편차에 영향을 줄 수 있으므로, 공정 능력(Cpk) 관점으로 관리하는 흐름이 안정적입니다.
2) 기준면 평행도와 높이 편차: 조립 뒤틀림을 만드는 누적 변수
스탠드오프는 단품 높이보다 “양단 기준면이 얼마나 평행한지”가 조립 평탄도에 더 직접적으로 작용할 수 있습니다. 다점 체결 구조에서는 높이 편차가 누적되어 PCB 휨, 하우징 간섭, 커넥터 삽입 불량으로 나타날 수 있습니다. 따라서 길이 공차와 평행도를 함께 관리하고, 조립 기준면을 도면에 명확히 지정하는 편이 유리합니다.
3) 탭/내경 동심도: 반복 체결 내구성의 숨은 변수
탭이 편심이면 체결 시 나사가 한쪽으로 끌리며 국부 마모와 풀림이 빠르게 나타날 수 있습니다. 동심도는 내경 가공, 탭 가공, 외형 가공의 기준 설정이 일치할 때 안정적으로 관리됩니다. 소형 부품일수록 기준 설정이 바뀌면 결과 편차가 커질 수 있어 공정 기준 통일이 중요합니다.
4) 디버링과 모서리 R: 기능성 외관과 안전성의 경계
육각 코너는 공구 흔적과 버가 가장 먼저 남는 영역이며, 조립 작업자의 취급성과 제품 손상 리스크를 동시에 좌우합니다. 미세 R 또는 디버링 기준을 과도하게 키우면 체결성이 떨어질 수 있어 기능 요구에 맞춘 균형이 필요합니다. 도면에 “허용 가능한 모서리 상태”를 문장으로 명확히 두면 검사와 납품 기준이 일관되어집니다.
스탠드오프와 같은 구조·연결 부품 흐름을 확장해 보려면 구조 · 연결용 부품 카테고리의 관련 사례를 함께 참고하면 문맥 연결에 도움이 됩니다. 가공 관점에서는 CNC 정밀 가공 페이지의 공차·가공결·디버링 기준과 품질기준 페이지의 검사 항목 구성 흐름을 함께 비교해 정리하는 방식도 유용합니다.