AgSnO₂ 접점 소재의 기술적 배경 및 AgCdO 대체 필요성

AgSnO₂ 접점과 AgCdO 접점
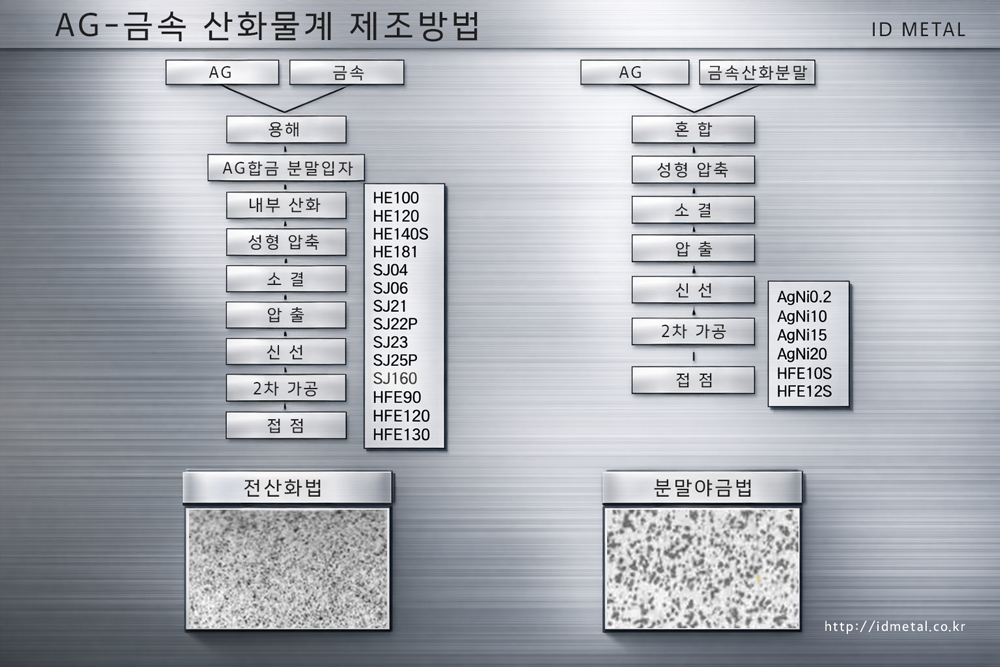
AgSnO₂ 접점 소재의 기술적 배경 및 AgCdO 대체 필요성
은 기반 금속산화물 접점은 개폐 과정에서 반복되는 아크, 접촉저항 변화, 용착 및 마모에 지속적으로 노출되는 핵심 기능 재료입니다. AgCdO는 오랜 기간 우수한 아크 내구성과 용착 저항으로 표준 접점 소재로 활용되었으나, 카드뮴의 독성 및 환경 규제 강화로 인해 대체 소재 개발이 필수적인 기술 과제가 되었습니다. AgSnO₂는 비독성 조성과 높은 내아크성, 내용착 특성을 동시에 확보할 수 있는 소재로 자리 잡았으며, 저전압 개폐기기 및 릴레이 분야에서 AgCdO를 대체하는 대표 소재로 적용이 확대되었습니다.
AgSnO₂ 접점은 온도 변화에 민감한 특성을 보이는데, 이는 SnO₂ 입자의 열 안정성과 관련되어 고온 환경에서 접촉 저항이 증가할 수 있습니다. AgSnO₂ 접점의 성능은 산화물 분산 상태, 계면 결합, 기공 및 미세조직 균일성에 크게 좌우되며, 이러한 요소는 제조 공정에 따라 결정적으로 달라집니다. 현재 산업적으로 가장 널리 활용되는 제조 공정은 전산화법(Internal Oxidation, IO)과 분말법(Powder Metallurgy, PM)입니다.
전산화법(Internal Oxidation)의 개요
전산화법은 Ag-Sn 합금 상태에서 산소를 확산시켜 내부 Sn을 선택적으로 산화하여 SnO₂ 입자를 Ag 매트릭스 내부에 형성하는 공정입니다. 이 공정은 합금 내부에서 직접 산화물이 생성되므로 산화물 입자의 미세화 및 균일 분산이 가능하며, 치밀하고 연속적인 Ag 매트릭스를 형성하는 특징이 있습니다.
전산화 공정의 핵심 특징은 다음과 같습니다.
산화물 입자가 수십~수백 nm 수준으로 미세 분산됩니다.
Ag와 SnO₂ 계면 결합력이 높아 전기적 연속성이 우수합니다.
접촉저항 및 온도 상승이 낮고 안정성이 높습니다.
고밀도 구조로 아크 침식 및 용착 저항이 뛰어납니다.
그러나 Sn 함량 증가 시 산소 확산 제한으로 산화 균일성이 저하되며, 제조 공정 시간이 길고 생산성이 낮다는 한계가 존재합니다. 또한 가공성 측면에서 경도가 증가하여 후가공 난이도가 높아질 수 있습니다.
분말법(Powder Metallurgy)의 개요
분말법은 Ag 분말과 SnO₂ 분말을 혼합한 후 성형 및 소결을 통해 복합재를 제조하는 방식입니다. 최근에는 기계적 합금화, 열간 압착, 진공 소결 등 다양한 공정이 적용되며, 분말 크기 및 분산 제어 기술 발전으로 성능 개선이 이루어지고 있습니다.
분말법의 특징은 다음과 같습니다.
조성 제어 및 산화물 함량 조절이 용이합니다.
대량 생산 및 복잡 형상 성형이 가능하여 산업적 유연성이 높습니다.
첨가제 도입 및 기능성 구조 설계가 용이합니다.
이종 금속 복합 구조 설계로 비용 절감 설계가 가능합니다.
반면 SnO₂ 입자의 응집 및 Ag 계면 젖음성 부족으로 인해 접촉저항 증가와 온도 상승 문제가 발생할 수 있으며, 기공 존재로 인해 전산화 소재 대비 내아크 성능이 다소 낮을 수 있습니다.
AgSnO₂가 AgCdO 대체재로 사용되는 이유
AgSnO₂는 AgCdO의 독성을 피하면서도 우수한 성능을 발휘합니다. AgCdO는 카드뮴 산화물(CdO)이 아크를 분산시키는 역할을 하지만, 환경 오염과 인체 유해성으로 인해 사용이 제한됩니다. 반면 AgSnO₂는 SnO₂의 열 안정성이 높아 고전류 환경에서 아크 침식 저항성이 더 우수합니다. 특히 램프나 커패시터 부하에서 전류 충격에 강하며, 재료 이동이 적어 DC 회로에서 안정적입니다. AgSnO₂는 AgCdO에 비해 용접 저항성이 높아 접점 고착을 방지합니다. 그러나 초기 접촉 저항이 약간 높아 온도 상승이 발생할 수 있으므로, 첨가제를 통해 이를 보완합니다.

전산화법 vs 분말법: 성능 및 전기적 특성 비교
두 공법으로 제조된 AgSnO₂ 접점은 아크 발생 시의 거동에서 확연한 차이를 보입니다. 전산화 접점은 산화물이 수지상(Dendritic) 구조를 형성하는 경향이 있어, 아크 침식에 대해 강한 저항성을 가집니다. 이는 고부하 차단 시 접점의 수명을 연장하는 요소가 됩니다. 반면 분말법 접점은 균일하게 분산된 산화물 입자가 아크의 족점(Arc Root)을 분산시켜 국부적인 용융을 억제하는 데 유리합니다.
온도 상승 측면에서 보면, 분말법은 접촉 저항이 상대적으로 일정하게 유지되는 특성이 있으나, 전산화법은 장기 사용 시 내부의 미산화 영역이나 편석으로 인해 저항이 불규칙하게 상승할 위험이 존재합니다. 하지만 전산화법은 입계 결합력이 우수하여 기계적 충격이 잦은 릴레이나 스위치에서 박리 현상이 적게 나타납니다.
| 구분 | 전산화 AgSnO₂ | 분말 AgSnO₂ |
|---|---|---|
| 제조 공정 특성 | Ag-Sn 합금 내부 산화에 의해 SnO₂ 형성 | Ag 분말과 SnO₂ 분말 혼합 후 성형·소결 |
| 미세조직 | 나노~미세 산화물 균일 분산, 고밀도 구조 / 표면 미세·내부 조대화 경향 | 산화물 응집 가능, 기공 존재 / 분말 크기 기반 균일 제어 가능 |
| 밀도 (g/cm³) | 9.8 ~ 10.0 | 9.7 ~ 9.9 |
| 경도 (HV) | 55 ~ 100 | 70 ~ 120 |
| 전기 전도도 (% IACS) | 81 ~ 83 | 75 ~ 82 |
| 접촉 저항 (mΩ) | 6 ~ 20 (낮고 안정적) | 40 ~ 80 (초기 높음, 사용 후 안정화) |
| 접촉 저항 안정성 | 중상 (장기 사용 시 일부 변동 가능) | 우수 (균일 조직 시 안정성 확보) |
| 내아크 / 아크 침식 저항 | 우수 (침상형 SnO₂ 구조에 의한 아크 분산) | 양호 (분산 최적화 시 개선) |
| 내용착성 (Anti-welding) | 우수 (고전류 조건에서 안정) | 매우 우수 (미세 분산 시 용착 억제 효과 큼) |
| 열 안정성 | 높음 (약 800°C까지 안정, 열전도 경로 연속) | 중간 (계면 저항 및 첨가제 영향) |
| 은-산화물 결합력 | 내부 산화 기반 화학적 결합으로 매우 강함 | 물리적 혼합·소결 결합으로 보통 수준 |
| 가공성 / 연성 | 합금 상태 가공으로 연성 양호하나 산화 후 경도 증가 | 경질 산화물 분산으로 가공 난이도 존재 |
| 산화물 입자 제어 | 공정 확산에 의존, 조성 증가 시 제어 제한 | 원료 분말 및 공정으로 입자·분산 제어 용이 |
| 최대 산화물 함량 | 약 10~12% 수준으로 제한 | 20% 이상 고농도 배합 가능 |
| 조성 설계 자유도 | 제한적 | 매우 우수 |
| 생산성 | 공정 시간 길고 생산성 낮음 | 대량 생산 적합 |
| 단가 | 고가 | 상대적으로 저가 |
온도 민감성 및 열적 특성
AgSnO₂ 접점은 온도 변화와 부하 특성에 매우 민감하게 반응합니다. 전산화법으로 제조된 접점은 주로 자동차용 릴레이, 가전제품의 메인 스위치 등 중간 정도의 부하에서 높은 기계적 신뢰성을 요구하는 곳에 적용됩니다. 재료 자체의 연성이 좋아 복잡한 형상의 단자로 가공하기에 용이하기 때문입니다. 반면 분말법 접점은 대전류를 차단해야 하는 산업용 접촉기(Contactor)나 차단기(Circuit Breaker)에 주로 사용됩니다. 특히 돌입 전류(Inrush Current)가 큰 램프 부하 혹은 모터 부하에서 분말법 특유의 균일한 산화물 분산은 접점의 용착을 방지하는 핵심적인 역할을 수행합니다. 신뢰성 측면에서 분말법은 대량 생산 시의 품질 균일도가 높다는 장점이 있으며, 전산화법은 접점의 박리나 균열에 대한 저항성이 높다는 평가를 받습니다.
AgSnO₂ 접점은 Ag의 높은 열전도성과 SnO₂의 내열성이 결합된 구조로 기본적인 열적 안정성은 우수합니다. 그러나 분말법 소재의 경우 계면 접촉저항 및 기공에 의해 국부 발열이 증가할 수 있으며, 이는 온도 민감 접점에서 열화 및 접촉저항 상승의 원인이 됩니다. 반면 전산화 소재는 연속적인 Ag 매트릭스와 균일 분산 산화물로 인해 열 확산 경로가 안정적이며 온도 상승 억제 효과가 나타납니다. 전산화 AgSnO₂는 고신뢰성, 낮은 접촉저항, 우수한 내아크 특성으로 장수명 접점 및 고부하 개폐 조건에서 강점을 보입니다. 다만 제조 비용과 생산성, 가공성 측면에서 제약이 존재합니다. 분말 AgSnO₂는 조성 설계 및 대량 생산성이 뛰어나며 비용 경쟁력이 높아 범용 릴레이 및 스위치 분야에서 폭넓게 사용됩니다. 그러나 균일 분산 및 계면 결합 문제로 고신뢰성 영역에서는 추가 합금화 및 공정 개선이 요구됩니다.
기술적 접근
AgSnO₂ 접점은 환경 대응형 접점 소재로서 AgCdO를 대체하는 핵심 기술이며, 제조 공정에 따라 성능 특성이 뚜렷하게 구분됩니다. 전산화 AgSnO₂는 균일 미세조직 기반의 고신뢰성 접점으로 고부하 및 장수명 조건에 적합하며, 분말 AgSnO₂는 조성 설계와 경제성이 강점으로 범용 전기기기 시장에서 높은 적용성을 갖습니다.
AgSnO₂는 AgCdO를 대체하는 것을 넘어, 이제는 독자적인 고성능 접점 재료로서 입지를 굳혔습니다. 전산화법은 강한 계면 결합력을 바탕으로 한 내구성을, 분말법은 설계의 유연성과 균일한 성능을 제공합니다. 최근에는 이 두 공법의 장점을 결합하여, 분말법으로 만든 잉곳을 다시 전산화 처리하거나 나노 복합 분말을 사용하는 등 소재의 한계를 극복하려는 시도가 계속되고 있습니다. 사용자는 장치의 정격 전류, 예상 수명, 가공 형상을 종합적으로 고려하여 최적의 공법을 선택해야 하며, 이는 곧 제품의 전기적 신뢰성으로 직결될 것입니다.
접점 설계에서는 단순 소재 선택보다 사용 부하, 온도 조건, 접촉력, 개폐 빈도 등을 종합적으로 고려하여 공정별 특성을 최적화하는 접근이 요구됩니다.
Technical Background of AgSnO₂ Contact Materials and the Need to Replace AgCdO
Silver-based metal oxide contacts are critical functional materials continuously exposed to arc erosion, contact resistance variation, welding, and mechanical wear during switching operations. AgCdO has long been used as a standard contact material due to its excellent arc resistance and anti-welding characteristics. However, the toxicity of cadmium and increasingly strict environmental regulations have made the development of alternative materials an essential technological requirement.
AgSnO₂ has emerged as a representative environmentally friendly substitute, combining non-toxic composition with high arc erosion resistance and anti-welding performance. Its application has expanded across low-voltage switching devices and relay systems where AgCdO was traditionally used.
AgSnO₂ contacts exhibit sensitivity to temperature variations, primarily associated with the thermal stability of SnO₂ particles. At elevated temperatures, contact resistance may increase due to microstructural evolution. The performance of AgSnO₂ contacts is strongly influenced by oxide dispersion, interfacial bonding, porosity, and microstructural uniformity. These factors are fundamentally determined by the manufacturing route, with Internal Oxidation (IO) and Powder Metallurgy (PM) being the most widely used industrial processes.
Overview of Internal Oxidation (IO)
Internal oxidation involves oxygen diffusion into an Ag-Sn alloy, selectively oxidizing Sn to form SnO₂ particles within the Ag matrix. Because oxide formation occurs in situ, extremely fine and uniform dispersion of oxide particles can be achieved, resulting in a dense and continuous silver matrix.
Key characteristics of the internal oxidation process include the formation of nanoscale to submicron oxide particles, strong Ag–SnO₂ interfacial bonding, low and stable contact resistance, and excellent resistance to arc erosion and welding due to the dense microstructure.
Nevertheless, increased Sn content may hinder oxygen diffusion, leading to incomplete oxidation and microstructural heterogeneity. Additionally, the process involves long oxidation cycles and limited productivity, while increased hardness can complicate subsequent machining.
Overview of Powder Metallurgy (PM)
Powder metallurgy involves blending Ag powder with SnO₂ powder followed by compaction and sintering to produce a composite material. Modern processing techniques such as mechanical alloying, hot pressing, and vacuum sintering have enhanced dispersion control and overall material performance.
Powder metallurgy offers flexibility in composition design and oxide content adjustment, enabling large-scale production and complex shape forming. The process also facilitates additive incorporation and functional composite design, contributing to cost-effective material solutions.
However, particle agglomeration and limited wettability between SnO₂ and Ag can lead to higher contact resistance and localized temperature rise. Residual porosity may also reduce arc resistance compared to internally oxidized materials.
Reasons Why AgSnO₂ Replaces AgCdO
AgSnO₂ provides comparable or superior performance without the environmental and health concerns associated with CdO. While CdO effectively disperses arc energy, regulatory restrictions on cadmium have accelerated the transition to alternative systems. SnO₂ exhibits high thermal stability and contributes to improved arc erosion resistance under high-current conditions.
AgSnO₂ demonstrates strong resistance to inrush current, particularly in lamp and capacitive loads, while minimizing material transfer and ensuring stable performance in DC circuits. Its enhanced anti-welding behavior prevents contact sticking, although slightly higher initial contact resistance may lead to temperature rise, which is typically mitigated through additives.
Performance and Electrical Characteristics: Internal Oxidation vs Powder Metallurgy
Contacts produced by these two processes show distinct arc behavior. Internally oxidized contacts often exhibit dendritic oxide structures that enhance arc erosion resistance and extend service life under heavy switching loads. Powder metallurgy contacts, on the other hand, benefit from uniformly dispersed oxide particles that distribute the arc root and reduce localized melting.
From a thermal standpoint, powder metallurgy materials tend to maintain relatively stable contact resistance, whereas internally oxidized materials may experience irregular resistance changes due to partially oxidized regions or segregation over long-term use. However, internally oxidized contacts possess strong intergranular bonding, reducing delamination under mechanical stress.
| Category | Internal Oxidation AgSnO₂ | Powder Metallurgy AgSnO₂ |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing principle | SnO₂ formed via oxidation inside Ag-Sn alloy | Mixing and sintering of Ag and SnO₂ powders |
| Microstructure | Fine oxide dispersion, dense matrix, surface fine / interior coarsening tendency | Possible agglomeration and porosity, particle size controllable |
| Density (g/cm³) | 9.8 ~ 10.0 | 9.7 ~ 9.9 |
| Hardness (HV) | 55 ~ 100 | 70 ~ 120 |
| Electrical conductivity (% IACS) | 81 ~ 83 | 75 ~ 82 |
| Contact resistance (mΩ) | 6 ~ 20, low and stable | 40 ~ 80 initially, stabilizes with use |
| Contact resistance stability | Moderate, potential variation over time | High with uniform structure |
| Arc erosion resistance | Excellent due to dendritic SnO₂ dispersion | Good, improved with optimized dispersion |
| Anti-welding performance | Strong under high current conditions | Very strong with fine oxide dispersion |
| Thermal stability | High, stable up to ~800°C | Moderate, affected by interface resistance |
| Ag–oxide bonding | Strong chemical bonding | Physical sintering bonding |
| Machinability / ductility | Good ductility pre-oxidation, increased hardness post-oxidation | Hard oxide dispersion complicates machining |
| Oxide particle control | Diffusion-controlled, limited at high Sn content | Easily controlled through powder processing |
| Maximum oxide content | Limited to ~10–12% | Can exceed 20% |
| Composition design flexibility | Limited | Very high |
| Productivity | Long processing time | Suitable for mass production |
| Cost | High | Relatively low |
Temperature Sensitivity and Thermal Characteristics
AgSnO₂ contacts are highly sensitive to temperature and load characteristics. Internally oxidized contacts are commonly used in automotive relays and household main switches requiring moderate load handling and high mechanical reliability. Their inherent ductility facilitates fabrication into complex terminal geometries.
Powder metallurgy contacts are frequently applied in high-current industrial contactors and circuit breakers. The uniformly dispersed oxide phase effectively suppresses welding under inrush current conditions typical of lamp or motor loads. In terms of reliability, powder metallurgy offers superior batch uniformity, whereas internal oxidation provides enhanced resistance to delamination and cracking.
AgSnO₂ combines the high thermal conductivity of silver with the heat resistance of SnO₂, resulting in intrinsically stable thermal behavior. However, interfacial resistance and porosity in powder metallurgy materials may cause localized heating and performance degradation in temperature-sensitive applications. Conversely, internally oxidized materials exhibit stable heat dissipation due to a continuous silver matrix and finely dispersed oxide particles, contributing to suppressed temperature rise.
Internally oxidized AgSnO₂ provides superior reliability, low contact resistance, and excellent arc resistance for long-life switching applications, although higher manufacturing cost and limited productivity remain constraints. Powder metallurgy AgSnO₂ offers strong cost competitiveness and design flexibility, making it widely suitable for general-purpose relays and switches, though high-reliability applications may require further alloying and process optimization.
추가 정보
이 섹션은 전산화법(Internal Oxidation)과 분말야금법(Powder Metallurgy)으로 제조되는 AgSnO₂ 접점의 미세조직, 접촉저항, 내용착, 열 거동 차이를 빠르게 정리합니다. 공정 선택 시에는 부하 유형(램프/모터/커패시터), 돌입전류, 허용 온도 상승, 장기 저항 안정성, 생산성·단가를 동시에 검토하는 것이 중요합니다.
핵심 포인트 요약
- 전산화법은 산화물이 합금 내부에서 형성되어 계면 결합이 강하고, 고밀도 구조로 내아크·내내용착 특성이 유리한 편입니다.
- 분말야금법은 조성 및 산화물 함량 설계 자유도가 높고, 대량 생산에 적합하여 비용 구조에서 장점이 나타납니다.
- 접촉저항과 온도 상승은 산화물 분산, 기공, Ag-산화물 계면 상태에 크게 좌우되며 공정 편차 관리가 신뢰성의 핵심입니다.
- 고돌입(램프/모터)·고전류 조건에서는 내용착 억제와 아크 루트 분산 설계가 접점 수명에 직접적으로 영향을 줍니다.
- 전산화법은 산소 확산 한계로 고함량 영역에서 미산화/편석 리스크가 생길 수 있으며, 분말야금법은 응집·젖음성 부족에 따른 초기 저항 상승을 관리해야 합니다.
- 열적 민감성(온도 상승, 국부 발열)은 기공 및 계면 저항이 커질수록 불리해지며, 표면 상태와 가공 이력까지 함께 평가하는 것이 바람직합니다.
- 현장 적용에서는 성능만이 아니라 공정 리드타임, 후가공 난이도, 품질 균일도(로트 간 편차)까지 포함한 총비용 관점이 필요합니다.
FAQ
AgSnO₂ 접점이 AgCdO를 대체하는 가장 큰 이유는 무엇인가요?
AgCdO는 아크 내구성과 내용착성이 우수하지만 카드뮴의 유해성 및 환경 규제 이슈가 있습니다. AgSnO₂는 비독성 계열로 전환 가능하며, 산화물의 열적 안정성과 아크 침식 저항을 기반으로 대체 적용이 확대되었습니다.
전산화법(Internal Oxidation) AgSnO₂가 유리한 적용 조건은 무엇인가요?
치밀한 Ag 매트릭스와 강한 Ag-산화물 결합이 확보되는 경우, 아크 침식과 내용착 억제가 중요한 조건에서 유리한 경향이 있습니다. 장기 사용 중 기계적 충격이나 진동이 동반되는 환경에서도 계면 박리 리스크가 상대적으로 낮게 설계될 수 있습니다.
분말야금법(Powder Metallurgy) AgSnO₂가 많이 채택되는 이유는 무엇인가요?
분말 혼합 기반이라 조성·산화물 함량 조절이 용이하고 대량 생산에 적합합니다. 또한 첨가제 적용과 분산 제어를 통해 부하 특성에 맞춘 설계가 가능해 산업 적용 범위가 넓습니다.
AgSnO₂ 접점의 온도 민감성은 어떤 요인에서 발생하나요?
접촉저항이 상승하면 국부 발열이 커지고 산화막 성장이나 미세조직 변화가 가속될 수 있습니다. 특히 기공, 계면 저항, 산화물 응집은 열 경로를 불안정하게 만들어 온도 상승과 저항 변동에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
전산화법과 분말야금법에서 접촉저항 안정성은 어떻게 달라지나요?
전산화법은 저항이 낮게 시작되는 경우가 많지만, 미산화 영역 또는 편석이 남을 경우 장기 변동 요인이 될 수 있습니다. 분말야금법은 초기 저항이 높게 나타날 수 있으나 분산·치밀화가 잘 확보되면 로트 간 균일도와 장기 안정성이 개선될 수 있습니다.
내용착(Anti-welding) 성능을 좌우하는 핵심 설계 요소는 무엇인가요?
아크 루트의 분산, 용융 영역의 국부화 억제, 산화물의 분포와 크기, 그리고 접촉면의 표면 상태가 핵심입니다. 부하 형태(AC/DC, 유도성/용량성, 돌입전류)와 접촉력 조건을 함께 고려해야 실사용에서의 내용착 리스크를 줄일 수 있습니다.
공정 선택 시 ‘성능’ 외에 어떤 기준을 함께 봐야 하나요?
공정 리드타임, 원재료 수급, 후가공 난이도, 품질 편차 관리, 검사 체계, 공급망 안정성을 함께 평가하는 것이 현실적입니다. 동일한 전기적 스펙이라도 로트 안정성과 생산성 차이가 총비용과 납기에 직접적으로 반영될 수 있습니다.
AgSnO₂ 접점은 어떤 장치에서 주로 사용되나요?
저전압 릴레이, 자동차 전장 릴레이, 가전 스위치, 산업용 접촉기 및 차단기 등 다양한 개폐 장치에 적용됩니다. 부하 조건과 요구 수명, 허용 온도 상승 기준에 따라 전산화법 또는 분말야금법이 선택됩니다.
관련 주제 확장
1) 미세조직과 아크 거동의 연결 고리
접점에서 아크는 순간적으로 높은 열 플럭스를 만들고, 용융·재응고를 반복시키며 표면 조도를 변화시킵니다. 이때 산화물의 분산 상태가 아크 루트(arc root) 이동과 에너지 분산에 영향을 주어 침식 패턴이 달라집니다. 전산화 기반 구조는 치밀한 매트릭스와 계면 결합으로 용융 확산과 재료 이동을 억제하는 방향으로 설계될 수 있습니다. 분말야금 기반 구조는 균일 분산이 확보되면 국부 용융을 완화하고 내용착 리스크를 줄이는 방향으로 접근됩니다.
2) 접촉저항, 온도 상승, 열화의 순환 구조
접촉저항이 커지면 발열이 증가하고 표면 산화 또는 미세조직 변화가 촉진될 수 있습니다. 이 변화가 다시 접촉저항을 키우는 방향으로 작동하면 장기 안정성이 급격히 저하될 수 있습니다. 따라서 초기 저항 관리(표면 상태, 분산·치밀화, 계면 저항 최소화)와 장기 저항 추적(부하 조건별 시험)이 함께 필요합니다.
3) 설계·생산 관점의 공정 선택 기준
전산화법은 공정 시간이 길고 산소 확산 제어가 중요하므로 생산성 및 단가에 부담이 생길 수 있습니다. 분말야금법은 대량 생산에 적합하지만 응집·기공·젖음성 문제를 정밀하게 제어해야 성능 편차를 줄일 수 있습니다. 최종 선택은 목표 수명, 부하 프로파일, 허용 온도 상승, 생산 규모, 후가공 난이도를 종합하여 결정하는 접근이 효율적입니다.
내부 링크로 이어지는 참고 흐름
전기접점 소재 관점의 추가 자료는 전기접점에서 함께 확인할 수 있으며, 공정·품질 관점의 기술 콘텐츠는 인사이트에 정리되어 있습니다. 접점 부품의 가공 관점에서는 CNC 정밀가공부품과 정밀프레스가공 부품의 공정 특성 비교가 도움이 되며, 체결 및 구조 설계 관점은 구조연결용 부품, 전장·배선 구성은 케이블와이어 하네스, 접합 공정 및 소재 관점은 브레이징 및 금속접합소재에서 연계해 살펴볼 수 있습니다.