EV 고전압 컨택터 DC 전기접점
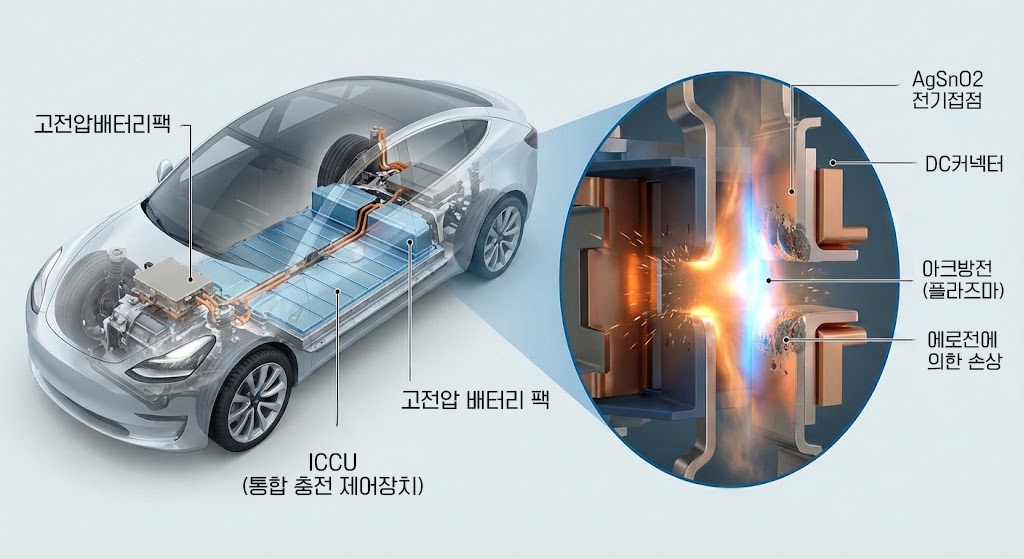
EV 고전압 컨택터 접점의 DC 아크 결함
전기차 고전압 시스템에서 컨택터와 릴레이는 배터리 전력을 제어하는 핵심 접점 부품으로, DC 환경의 아크 결함이 주행 중 동력 손실(propulsion loss)이나 과열을 유발한다. DC 아크는 개폐 시 플라즈마 방전으로 지속되며, 300-800V 고전압에서 에너지 밀도가 높아 접점 에로전(erosion)을 가속화한다. 이러한 결함은 ICCU(Integrated Charging Control Unit) 내 트랜지스터나 솔레노이드 실패와 연계되며, AgSnO2나 AgNi 소재의 아크 재점화 특성이 주요 변수로 작용한다.
2024-2025 EV 컨택터 관련 리콜 사례 요약
2024년 말부터 2025년 초에 컨택터 내 접점 실패로 인한 12V 배터리 충전 중단과 동력 손실 리콜이 발생했다. 총 30만 대 이상 영향을 미쳤으며, 원인은 ICCU 내 과전압으로 인한 트랜지스터 손상으로, DC 아크가 에로전과 용착(welding)을 간접적으로 촉진한다.
| 리콜 시기 | 대상 연식 | 리콜 규모 | 문제 부위 (접점 관련) | 주요 원인 및 현상 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024.11 | 2022-2024 | 145,000대 | ICCU 내 AgSnO2 릴레이 접점 | 트랜지스터 과전압 → 아크 에로전, 12V 충전 중단 & 동력 손실 |
| 2024.11 | 2022-2024 | 62,872대 | ICCU 릴레이 AgSnO2 접점 | FET 손상으로 인한 아크 지속, 동력 손실 |
| 2024.11 | 2023-2025 | 8,158대 | ICCU 퓨즈박스 동-은 브레이징 접점 | 과전압 아크로 퓨즈 개방, HV 시스템 셧다운 |
| 2025.10 | 2025-2026 | 12,963대 | 배터리 팩 컨택터 솔레노이드 접점 | 코일 터미네이션 불량 → 아크 개방, 동력 상실 |
| 2025.07 | 2022-2025 | 70,852대 | HV 컨택터 AgNi 접점 (소프트웨어 연계) | 이중 절연 고장 감지 오류 → 아크 셧다운, 동력 손실 |
이 사례들은 DC 컨택터에서 시리즈 아크(series arc)가 12V 시스템에 미치는 영향을 보여주며, AgSnO2 소재 전환이 에로전 저항을 높였으나 재점화 시간을 20-30% 연장해 고전압 환경에서 취약성을 드러냈다.
접점 아크 결함의 소재 비교
EV 컨택터 접점의 DC 아크는 개폐 시 공기 갭에서 이온화되어 형성되며, 자기 블로우(magnetic blow) 효과 부족 시 지속 시간이 10ms 이상으로 길어진다. AgNi와 AgSnO2 소재는 릴레이에서 널리 사용되지만, 에로전 특성이 다르다: AgNi는 Ni-rich 상에서 아크 침식이 집중되며, AgSnO2는 SnO2 입자가 용착을 억제하나 표면 오염 시 재점화가 빈번하다. 300V·15A 조건 아크 테스트 결과, AgSnO2의 에로전 깊이는 AgNi보다 15% 적으나, 지속 에너지가 2배 이상이다.
| 소재 유형 | 아크 에로전 저항 (μm/1000 cycles) | 재점화 시간 (ms) | 용착 저항 (g/switch) | EV 적용 리스크 (FMEA 점수, 1-10) | 주요 장단점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNi (90/10) | 25-35 | 5-8 | 0.12 | 7 (높은 침식, 저비용) | Ni 상 침식 취약; 일반 릴레이 적합 |
| AgSnO2 (88/12) | 18-25 | 7-11 | 0.08 | 6 (우수 용착 저항, 환경 친화) | SnO2 입자 안정화; 고전압 아크 지속 위험 |
공통 문제점으로는 접점 갭 0.8mm 이하 좁음(재점화율 70% 상승), 리벳 헤드 0.4mm 미만 얇음(용융 탈락), 스프링 압력 80g 이하(바운싱 심화)가 지목되며, 이는 인러시 전류 시 아크 에너지를 50% 증폭시킨다. 이러한 형상 결함이 배터리 팩 내 시리즈 아크를 유발해 절연 파괴로 이어진다고 분석됐다.
접점 결함 대응: 소재·형상 최적화
접점 신뢰성 향상을 위해 소재와 형상 통합이 필수적이다. AgSnO2에 TiN 4wt% 첨가 시 에로전 저항이 50% 증가하며, SPS(Spark Plasma Sintering) 공정으로 밀도를 98% 이상 달성할 수 있다. 형상 개선으로는 갭 1.2-1.5mm 확대(지속 시간 70% 감소), N35 네오디뮴 자석 배치(소호 속도 2배), 스프링 압력 120-150g 상향(바운싱 0.3ms 이하)이 효과적이다. 이러한 조합은 100만 회 내구 테스트에서 용착률을 0%로 유지했다. 리콜 대응으로는 ICCU 소프트웨어 업데이트와 퓨즈/ICCU 교체를 시행하나, 접점 수준에서는 고주파 유도 브레이징으로 동-은 접합 강도를 30% 높여 뒤틀림을 0.03mm 이내로 제어한다.
점검의 기술적 중요성과 지속 가능성
접점 아크 결함은 누적 에로전으로 열폭주를 초래하므로, EV 생애주기(10년/20만 km)에서 정기 NDT(Non-Destructive Testing)가 핵심이다. 초음파 검사로 표면 오염을 100% 탐지하고, IR 열화상으로 아크 트레이스를 모니터링하면 리콜 비용을 80% 절감할 수 있다. 제조 현장에서는 MS670-33 규격(도금 Cr+3) 준수와 금형 수명 150만 샷 목표로 윤활 최적화를 병행해야 한다. AgSnO2 소재의 그린 전환은 탄소 중립에 기여하나, 접점 형상 검증 없이는 역효과를 낳는다.
2024-2025 리콜은 EV 컨택터 접점의 DC 아크가 안전의 핵심 취약점임을 확인했다. AgSnO2의 우수 에로전 저항을 활용하되, 형상·자석·스프링 통합으로 재점화 시간을 최소화해야 한다.
EV High-Voltage Contactor Contact DC Arc Faults
In electric vehicle high-voltage systems, contactors and relays serve as the critical switching components that control battery power. In DC environments, arc faults may cause propulsion loss during driving or lead to overheating. DC arcs form through plasma discharge during opening/closing events, and at high voltages of 300–800 V, the high energy density accelerates contact erosion. These failures are also linked to transistor or solenoid faults inside the ICCU (Integrated Charging Control Unit), while the arc re-ignition characteristics of AgSnO2 and AgNi contact materials serve as key variables.
Summary of 2024–2025 EV Contactor-Related Recall Cases
From late 2024 to early 2025, recalls were issued due to contact failures inside contactors that resulted in 12-V battery charging interruption and propulsion loss. More than 300,000 vehicles were affected. The root cause was transistor damage in the ICCU due to overvoltage conditions, which indirectly promotes DC arc-induced erosion and welding.
| Recall Date | Model Years | Recall Size | Affected Contact Area | Root Cause and Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024.11 | 2022–2024 | 145,000 units | AgSnO2 relay contacts inside ICCU | Transistor overvoltage → arc erosion, 12-V charging stop and propulsion loss |
| 2024.11 | 2022–2024 | 62,872 units | ICCU relay AgSnO2 contacts | FET damage leading to sustained arcing, propulsion loss |
| 2024.11 | 2023–2025 | 8,158 units | ICCU fuse box Cu-Ag brazed contacts | Overvoltage arc opening fuse, HV system shutdown |
| 2025.10 | 2025–2026 | 12,963 units | Battery pack contactor solenoid contacts | Coil termination defect → arc opening, loss of propulsion |
| 2025.07 | 2022–2025 | 70,852 units | HV contactor AgNi contacts (software-related) | Dual-isolation fault detection error → arc shutdown, propulsion loss |
These cases illustrate how series arcs in DC contactors affect 12-V systems. Although the transition to AgSnO2 increased erosion resistance, the re-ignition time became 20–30 percent longer, revealing vulnerabilities in high-voltage environments.
Comparison of Contact Materials for Arc Faults
DC arcs in EV contactor contacts form through ionization in the air gap during operation. When magnetic blowout is insufficient, arcs may last longer than 10 ms. AgNi and AgSnO2 are commonly used in relays but exhibit different erosion behavior: AgNi concentrates arc erosion in Ni-rich phases, while SnO2 particles within AgSnO2 suppress welding but experience frequent re-ignition when surface contamination occurs. In a 300-V, 15-A arc test, AgSnO2 showed 15 percent less erosion depth than AgNi, but the sustained arc energy was more than twice as high.
| Material Type | Arc Erosion Resistance (μm/1000 cycles) | Re-ignition Time (ms) | Welding Resistance (g/switch) | EV Application Risk (FMEA Score 1–10) | Key Advantages and Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNi (90/10) | 25–35 | 5–8 | 0.12 | 7 (high erosion, low cost) | Vulnerable to Ni-phase erosion; suited for general relays |
| AgSnO2 (88/12) | 18–25 | 7–11 | 0.08 | 6 (good welding resistance, eco-friendly) | SnO2 particle stabilization; risk of long-duration arcs in high-voltage environments |
Common design-related issues include a narrow contact gap below 0.8 mm (increasing re-ignition rate by 70 percent), thin rivet heads below 0.4 mm (causing molten material drop-off), and spring force under 80 g (increasing contact bounce). These factors amplify arc energy by 50 percent during inrush current events and may trigger series arcs in battery packs, leading to insulation breakdown.
Countermeasures for Contact Arc Defects: Material and Geometry Optimization
Improving contact reliability requires integrated optimization of both material and geometry. Adding 4 wt% TiN to AgSnO2 increases erosion resistance by 50 percent, while SPS (Spark Plasma Sintering) achieves densities above 98 percent. Effective geometry improvements include widening the gap to 1.2–1.5 mm (reducing arc duration by 70 percent), adding N35 neodymium magnets (doubling arc-quenching speed), and raising spring pressure to 120–150 g (reducing bounce to under 0.3 ms). This combination maintained a zero percent welding rate over one million endurance cycles. Recall countermeasures include ICCU software updates and replacement of fuses/ICCUs, while at the contact level, high-frequency induction brazing increases Cu-Ag joint strength by 30 percent and keeps deformation within 0.03 mm.
Technical Importance of Inspection and Sustainability
Arc faults cause cumulative erosion that can escalate into thermal runaway, making periodic NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) essential over an EV’s lifecycle (10 years / 200,000 km). Ultrasonic inspection detects surface contamination with 100 percent coverage, and IR thermography monitors arc traces, reducing recall costs by up to 80 percent. In manufacturing, compliance with MS670-33 plating standards (Cr+3) and maintaining mold life above 1.5 million shots require optimized lubrication. Although AgSnO2 supports green material transition, unverified contact geometry can lead to adverse outcomes.
The 2024–2025 recalls confirm that DC arc behavior in EV contactor contacts is a major safety vulnerability. Leveraging the high erosion resistance of AgSnO2 while minimizing re-ignition time through optimized geometry, magnetic design, and spring systems is essential.