전자접촉기용 퀵 커넥트 콘택터와 CNC 정밀 접속 부품
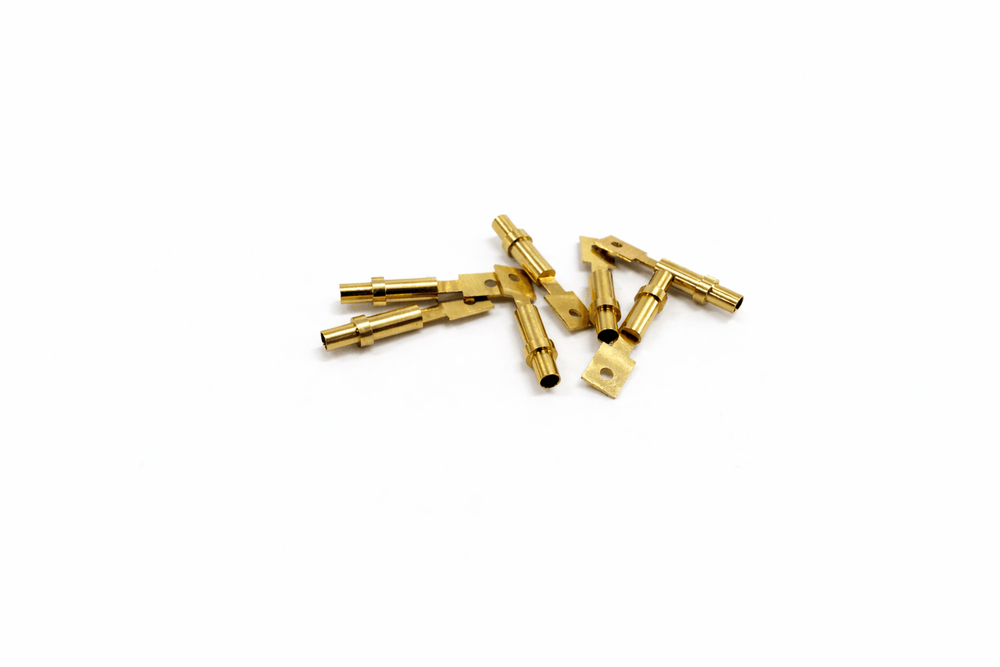

전자접촉기용 퀵 커넥트 콘택터 CNC 정밀 접속 부품
퀵 커넥트 콘택터(Quick Connect Contactor)는 전자접촉기 내부에서 전원 라인과 접점 모듈, 또는 외부 배선과 내부 전류 경로를 빠르고 재현성 있게 연결하기 위해 사용되는 접속 구조입니다. 이 방식은 볼트 체결이나 납땜 방식과 달리, 일정 형상의 블레이드(Blade)와 소켓이 기계적으로 맞물리며 접촉 압력에 의해 전기적 연결을 유지하는 것이 특징입니다.
전자접촉기와 같이 빈번한 스위칭이 발생하는 장비에서는 접속부의 안정성이 곧 전체 장비의 신뢰성으로 직결되므로, 퀵 커넥트 콘택터 내부를 구성하는 개별 부품의 정밀도가 매우 중요합니다.
퀵 커넥트 콘택터 내부 구조
퀵 커넥트 콘택터는 일반적으로 블레이드형 단자와 이를 수용하는 스프링 접촉 구조로 구성됩니다. 블레이드는 전류를 전달하는 고정 접속부 역할을 하며, 소켓 측의 스프링 접점은 일정한 접촉 압력을 유지하면서 탈착을 가능하게 합니다.
이 구조에서 핵심은 블레이드의 치수 정밀도와 표면 상태입니다. 블레이드 폭, 두께, 평행도, 단부 형상은 삽입력과 유지력을 직접적으로 결정하며, 이 값이 설계 범위를 벗어나면 접촉 압력 불균형, 미세 미끄럼, 접촉저항 불안정이 발생합니다. 따라서 퀵 커넥트 콘택터는 단순한 단자가 아니라, 반복 결합 환경을 전제로 한 정밀 기계 요소로 취급됩니다.
퀵 커넥트 콘택터에 사용되는 CNC 가공 부품 커넥터
전자접촉기용 퀵 커넥트 콘택터 내부에는 블레이드와 하우징을 연결하거나, 전류를 내부 접점부로 전달하는 CNC 가공 부품이 사용됩니다. 이 부품은 단순한 지지용 부품이 아니라, 전류 경로의 일부이자 접촉 안정성을 좌우하는 핵심 구성 요소입니다.
빈번한 스위칭이 발생하는 장비에서는 순간 전류와 반복 열 사이클이 발생하므로, 이 CNC 부품은 전기적 전도성, 열 전달, 기계적 강성을 동시에 만족해야 합니다.
쾌삭 황동을 사용한 CNC 가공 부품은 절삭성이 우수해 치수 편차를 최소화할 수 있으며, 블레이드 삽입부와 결합부를 정밀하게 구현할 수 있다는 장점이 있습니다.

CNC 가공 정밀도가 접촉 신뢰성에 미치는 영향
퀵 커넥트 콘택터에서 접촉 불량의 상당 부분은 접점 소재 자체보다, 이를 지지하고 연결하는 CNC 가공 부품의 정밀도 부족에서 발생합니다. 블레이드가 연결되는 부위의 동심도나 평행도가 미세하게 어긋나면, 소켓 스프링 접점과의 접촉이 한쪽으로 치우치게 되고, 이로 인해 국부 접촉 저항 상승과 비대칭 마모가 발생합니다. 이러한 현상은 초기에는 감지되지 않더라도, 반복 스위칭 환경에서는 점진적으로 열화가 누적됩니다. 또한 가공 표면의 미세한 버나 가공 흔적은 삽입 시 소켓 접점을 긁어 표면 도금 손상을 유발할 수 있으며, 이는 접촉 저항 증가와 미세 분진 발생으로 이어질 수 있습니다. 따라서 CNC 가공 부품은 외관 품질보다 접촉 안정성 관점에서 표면 관리가 이루어져야 합니다.
쾌삭 황동 재질
퀵 커넥트 콘택터용 접속 부품에 쾌삭 황동이 사용되는 이유는 단순히 가공이 쉽기 때문이 아닙니다. 황동은 구리 기반 합금으로 전기 전도성이 확보되며, 절삭성이 좋아 미세 형상과 반복 생산 시 치수 안정성이 우수합니다.
이는 블레이드 결합부, 원통형 체결부, 내부 전류 전달부를 하나의 부품으로 일체화하는 설계에 유리하며, 조립 공정 단순화와 접촉 신뢰성 확보에 기여합니다.
다만 황동은 표면 산화와 마찰 마모에 민감할 수 있으므로, 퀵 커넥트 콘택터용 부품에서는 표면 거칠기 관리와 도금 전 전처리 품질이 중요하게 작용합니다. 이 부품은 직접적인 스위칭 아크를 담당하지 않더라도, 전류 경로 상에 위치하기 때문에 표면 상태가 장기 접촉 안정성에 영향을 미칩니다.
빈번한 스위칭 환경
모터제어센터와 같이 반복 개폐가 이루어지는 환경에서는 접점부뿐 아니라 접속 부품 전체가 미세한 열 팽창과 수축을 반복합니다. 이 과정에서 CNC 접속 부품은 단순한 구조물 역할을 넘어, 열을 분산시키고 전류를 안정적으로 전달하는 역할을 수행합니다.
부품 단면이 불균일하거나 급격한 형상 변화가 있을 경우, 국부 발열이 집중되어 접촉 안정성 저하로 이어질 수 있으므로, 전자접촉기용 퀵 커넥트 콘택터 부품은 열과 전류 흐름을 동시에 고려한 형상 설계가 요구됩니다.

| 구분 | 관리 대상 | 콘택터 성능에 미치는 영향 | 주요 관리 포인트 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 치수 정밀도 | 블레이드 결합부 폭·두께·평행도 | 삽입력·유지력 안정성 | 공차 관리, 기준면 일관성 |
| 표면 상태 | 접촉면 인접부 거칠기·버 | 접촉저항 안정성 | 디버링, 가공결 방향 관리 |
| 형상 설계 | 단면 변화, 코너 처리 | 발열 및 응력 집중 | 미세 R 처리, 단면 연속성 |
| 소재 특성 | 쾌삭 황동 조직 | 전도성·열 전달 | 합금 관리, 일관된 소재 사용 |
| 조립 재현성 | 결합부 정렬성 | 반복 탈착 신뢰성 | 가이드 형상, 치수 반복성 |
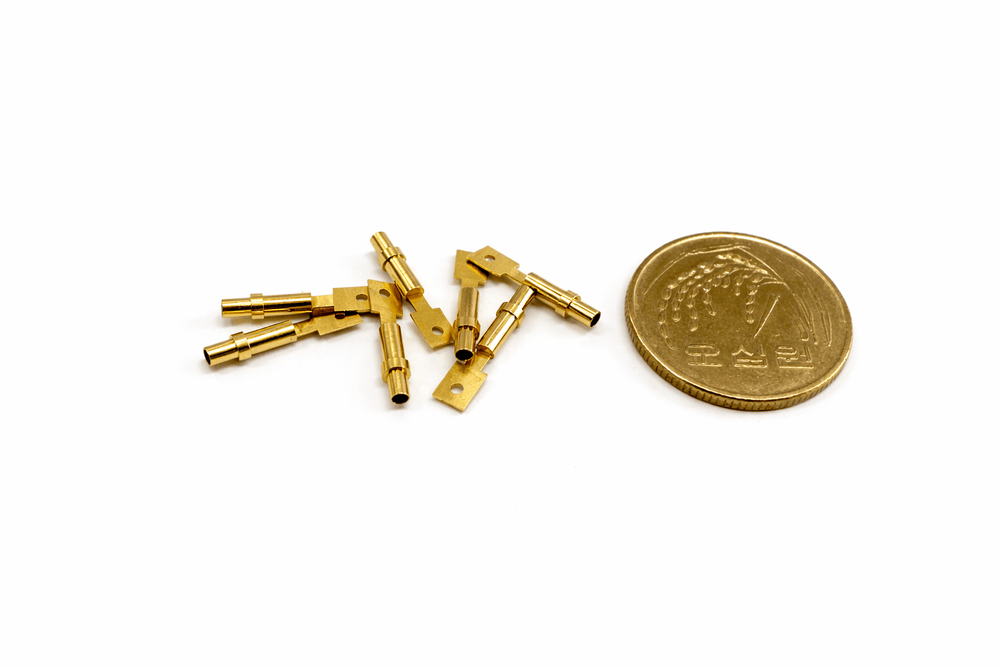

퀵 커넥트 콘택터는 전자접촉기 내부에서 빠른 조립과 안정적인 전기 연결을 동시에 요구받는 접속 구조입니다. 이 구조의 신뢰성은 접점 소재뿐 아니라, 그 접점을 지지하고 전류를 전달하는 CNC 정밀 부품의 완성도에 의해 좌우됩니다.
쾌삭 황동으로 CNC 가공된 접속 부품은 치수 안정성과 생산성을 확보하는 동시에, 반복 스위칭 환경에서 접촉 압력과 전류 흐름을 안정화하는 역할을 수행합니다. 따라서 이 부품은 단순한 기계 부품이 아니라, 전자접촉기용 퀵 커넥트 콘택터의 성능을 구조적으로 뒷받침하는 핵심 정밀 부품으로 이해하는 것이 타당합니다.
Quick Connect Contactors for Electromagnetic Contactors and CNC Precision Connection Components
Quick Connect contactors are connection structures used inside electromagnetic contactors to reliably and repeatedly connect power lines with contact modules, or external wiring with internal current paths.
Unlike bolted joints or soldered connections, this structure relies on a mechanically engaged blade and socket interface, where electrical continuity is maintained through controlled contact pressure.
In equipment such as electromagnetic contactors, where switching operations occur frequently, the stability of the connection interface directly affects the overall reliability of the system. For this reason, the dimensional accuracy and surface integrity of the individual components forming the quick connect contactor are critical.
Internal Structure of a Quick Connect Contactor
A quick connect contactor typically consists of a blade-type terminal and a corresponding spring-loaded contact structure that receives it.
The blade functions as a fixed current-carrying interface, while the socket-side spring contact maintains consistent contact pressure and allows repeated insertion and removal.
Within this structure, the dimensional accuracy and surface condition of the blade are the key performance determinants. Blade width, thickness, parallelism, and edge geometry directly influence insertion force and retention force. When these parameters deviate from their design range, contact pressure imbalance, micro-sliding, and unstable contact resistance may occur.
For this reason, a quick connect contactor is not treated as a simple terminal but rather as a precision mechanical interface designed for repeated mating cycles.
CNC-Machined Connection Components Used in Quick Connect Contactors
Inside electromagnetic contactors, CNC-machined components are used to connect the blade to the housing or to transmit current from the blade to the internal contact assembly.
These components are not merely structural supports; they form part of the electrical current path and play a decisive role in maintaining contact stability.
In systems subject to frequent switching, instantaneous current surges and repeated thermal cycling are inevitable. As a result, these CNC-machined components must simultaneously satisfy requirements for electrical conductivity, thermal dissipation, and mechanical rigidity.
CNC-machined components made from free-cutting brass offer excellent machinability, allowing tight dimensional tolerances to be maintained while precisely forming blade insertion interfaces and connection features. This contributes directly to consistent assembly quality and stable insertion behavior.
Influence of CNC Machining Accuracy on Contact Reliability
In quick connect contactors, a significant portion of contact failures originate not from the contact material itself, but from insufficient precision in the CNC-machined components that support and align the contact interface.
If concentricity or parallelism at the blade connection area deviates even slightly, contact pressure within the socket spring becomes uneven. This leads to localized increases in contact resistance and asymmetric wear. While such issues may not be immediately apparent during initial operation, they accumulate progressively under repeated switching conditions.
In addition, microscopic burrs or machining marks on the surface can scratch the socket contact during insertion, damaging surface plating and generating metallic debris. This debris can migrate into the contact interface, increasing resistance and accelerating wear.
Therefore, CNC-machined components must be managed from a contact reliability perspective rather than solely based on visual appearance.
Free-Cutting Brass as a Material for Quick Connect Contact Components
The use of free-cutting brass in quick connect contactor connection components is not solely driven by ease of machining.
As a copper-based alloy, brass provides sufficient electrical conductivity while offering superior machinability, enabling stable dimensional control and high repeatability in mass production.
This material characteristic allows blade interfaces, cylindrical connection sections, and internal current-carrying features to be integrated into a single component. Such integration simplifies assembly processes and enhances contact reliability.
However, brass is relatively sensitive to surface oxidation and frictional wear. For this reason, surface roughness control and plating pre-treatment quality are critical for quick connect contactor components.
Even when the component does not directly handle switching arcs, its position within the current path means that surface condition has a direct influence on long-term contact stability.
Functional Role of CNC Connection Components in Frequent Switching Environments
In environments such as motor control centers, where repeated switching occurs, not only the contact points but the entire connection assembly undergoes continuous thermal expansion and contraction.
Under these conditions, CNC-machined connection components act not merely as mechanical structures but also as elements that distribute heat and stabilize current flow.
If the component cross-section is uneven or includes abrupt geometric transitions, localized heat concentration can occur, leading to degradation of contact stability.
Accordingly, quick connect contactor components for electromagnetic contactors require geometric designs that consider both thermal behavior and current flow simultaneously.
Key Control Parameters for CNC Precision Components Used in Quick Connect Contactors
| Category | Controlled Feature | Impact on Contactor Performance | Key Control Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Accuracy | Blade interface width, thickness, parallelism | Stability of insertion and retention force | Tolerance control, consistent datum definition |
| Surface Condition | Roughness and burrs near contact areas | Contact resistance stability | Deburring process control, machining direction management |
| Geometric Design | Section transitions, corner treatment | Heat concentration and stress distribution | Micro-radius application, continuous cross-section design |
| Material Properties | Free-cutting brass microstructure | Electrical conductivity and heat transfer | Alloy consistency, material traceability |
| Assembly Repeatability | Alignment of connection interfaces | Reliability under repeated mating cycles | Guide geometry optimization, dimensional repeatability |
Conclusion
Quick connect contactors provide both rapid assembly and stable electrical connection within electromagnetic contactors. The reliability of this structure depends not only on the contact material itself, but also on the precision and integrity of the CNC-machined components that support and transmit current.
CNC-machined connection components produced from free-cutting brass ensure dimensional stability and manufacturing efficiency while stabilizing contact pressure and current flow under frequent switching conditions.
Accordingly, these components should be regarded not as simple mechanical parts, but as critical precision elements that structurally support the performance and reliability of quick connect contactors used in electromagnetic contactors.
추가 정보
퀵 커넥트 콘택터 CNC 정밀 접속 부품은 전자접촉기 내부에서 전원 라인과 접점 모듈(또는 외부 배선과 내부 전류 경로)을 빠르고 재현성 있게 연결하기 위한 접속 인터페이스를 구성합니다. 반복 결합과 빈번한 스위칭 환경에서는 블레이드-소켓 접촉 압력의 균일성, 접촉저항 안정성, 열 사이클 내구성이 함께 평가 포인트가 됩니다.
핵심 포인트
- 블레이드 폭·두께·평행도는 삽입력과 유지력, 접촉 압력 균일성에 직접 영향을 줍니다.
- 동심도·평행도 불일치는 한쪽 접촉 편중을 유발해 국부 저항 상승과 비대칭 마모로 이어질 수 있습니다.
- 가공 버(burr)·미세 흠집·가공결은 삽입 과정에서 도금 손상과 금속 분진 발생의 원인이 됩니다.
- 전류 경로 상에 위치하는 연결 부품은 전도성뿐 아니라 열 확산(열 분산) 관점의 단면 설계가 중요합니다.
- 쾌삭 황동(Free-cutting brass)은 절삭성이 좋아 치수 반복성과 생산 재현성 확보에 유리합니다.
- 황동은 산화와 마찰 마모에 민감할 수 있어 표면 거칠기 관리와 도금 전 전처리 품질이 변수로 작용합니다.
- 급격한 단면 변화나 날카로운 코너는 국부 발열·응력 집중을 유발할 수 있어 미세 R 처리와 단면 연속성이 유리합니다.
FAQ
퀵 커넥트 콘택터는 왜 볼트 체결이나 납땜 대신 사용하나요?
블레이드와 소켓이 기계적으로 맞물리며 접촉 압력으로 전기적 연속을 유지해, 조립 속도와 반복 탈착성 측면에서 유리합니다. 다만 이 방식은 치수·표면 상태에 민감하므로 정밀 가공과 품질 관리가 핵심입니다.
접촉 불량은 접점 소재 문제보다 가공 정밀도 문제일 때가 많나요?
실제로 접점 소재 자체보다, 이를 지지·정렬하는 CNC 접속 부품의 동심도·평행도 불량에서 시작되는 사례가 적지 않습니다. 접촉 압력이 편중되면 국부 저항이 상승하고 반복 스위칭에서 열화가 누적될 수 있습니다.
버(burr)나 가공 흔적은 왜 접촉 신뢰성에 불리한가요?
미세 버나 거친 가공결은 삽입 시 소켓 스프링 접점을 긁어 도금 손상을 유발할 수 있습니다. 도금 손상과 분진은 접촉저항 증가, 마모 가속, 미세 미끄럼(micro-sliding) 리스크를 키웁니다.
쾌삭 황동이 퀵 커넥트 콘택터 연결 부품에 자주 쓰이는 이유는 무엇인가요?
구리 기반 합금으로 전도성이 확보되면서 절삭성이 좋아 미세 형상 구현과 치수 안정성(반복 생산성)에 유리합니다. 블레이드 결합부와 체결부, 내부 전류 전달부를 일체화하는 설계에서도 생산 재현성을 확보하기 쉽습니다.
황동 부품에서 표면 산화나 마찰 마모는 어떻게 고려하나요?
황동은 산화와 마찰 마모에 민감할 수 있어 표면 거칠기 관리와 도금 전 전처리 품질이 중요해집니다. 스위칭 아크를 직접 담당하지 않더라도 전류 경로 상의 표면 상태가 장기 접촉 안정성에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
빈번한 스위칭 환경에서 연결 부품은 어떤 역할을 하나요?
반복 개폐 환경에서는 전체 조립체가 열 팽창·수축을 반복하므로, 연결 부품은 전류 전달과 함께 열 분산 요소로도 작동합니다. 단면이 불균일하거나 급격한 형상 변화가 있으면 국부 발열이 집중되어 접촉 안정성 저하로 이어질 수 있습니다.
설계/가공 단계에서 가장 먼저 점검할 치수 항목은 무엇인가요?
블레이드 인터페이스의 폭·두께·평행도, 결합부의 동심도, 기준면(datum) 일관성이 우선 점검 포인트가 됩니다. 해당 항목이 흔들리면 삽입력·유지력·접촉저항이 동시에 변동할 수 있습니다.
외관보다 “접촉 안정성 관점”의 표면 관리란 무엇을 의미하나요?
단순 광택이나 보기 좋은 표면이 아니라, 삽입/탈착 과정에서 접점 도금 손상과 분진 발생을 줄이는 방향의 표면 품질을 뜻합니다. 디버링, 가공결 방향 관리, 미세 R 처리 등 기능 중심의 관리 항목이 포함됩니다.
관련 주제 확장
1) 공차 설계와 기준면 관리: 조립 재현성의 출발점
퀵 커넥트 구조는 “결합이 된다”보다 “결합이 늘 같은 품질로 된다”가 중요합니다. 블레이드 결합부의 폭·두께·평행도와 결합부 정렬성은 삽입력과 유지력의 변동폭을 좌우합니다. 기준면이 바뀌거나 측정 기준이 흔들리면, 동일한 공정 조건에서도 조립 품질이 흔들릴 수 있습니다. 초기 불량이 보이지 않더라도 반복 결합과 열 사이클에서 편차가 누적되는 형태로 나타날 수 있습니다.
2) 디버링과 표면 거칠기: 도금 손상과 미세 분진 리스크
삽입 시 접촉부는 미끄럼과 국부 압착이 동시에 발생할 수 있어, 표면의 미세 결함이 기능 문제로 직결됩니다. 버(burr)나 날카로운 엣지는 소켓 스프링 접점을 긁어 도금 손상과 금속 분진을 만들 수 있습니다. 결과적으로 접촉저항이 증가하고 비대칭 마모가 진행되면, 반복 스위칭에서 열화 속도가 빨라질 수 있습니다. 표면 관리는 외관 중심이 아니라 접촉 안정성과 장기 저항 안정성 관점에서 설계·가공·검사 단계가 연결되어야 합니다.
3) 열과 전류 흐름을 함께 보는 형상 설계
빈번한 스위칭 환경에서는 순간 전류와 반복 열 사이클이 누적되며, 연결 부품의 단면 변화가 발열 분포에 영향을 줍니다. 급격한 단면 변화나 코너는 국부 발열 및 응력 집중을 유발할 수 있어, 미세 R 처리와 단면 연속성이 유리합니다. 전류 경로 상에서 접속부의 안정성은 단순 전도성뿐 아니라 열 확산 경로 확보와도 연관됩니다. 따라서 CNC 정밀 접속 부품은 전기적·열적·기계적 요구 사항을 동시에 만족하는 형태로 접근하는 편이 합리적입니다.
전자접촉기, 릴레이, 커넥터 등 접점 관점의 신뢰성 이슈를 함께 정리하려면 전기 접점(Contacts) 카테고리의 관련 글을 함께 참고하면 문맥 연결에 도움이 됩니다. 또한 구조·연결용 부품 흐름에서 정밀 결합 요소를 확장하려면 구조 · 연결용 부품 카테고리의 사례를 함께 비교할 수 있습니다.